
- #DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB HOW TO#
- #DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB MANUAL#
- #DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB SOFTWARE#
- #DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB SERIES#
#DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB SERIES#
#DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB MANUAL#
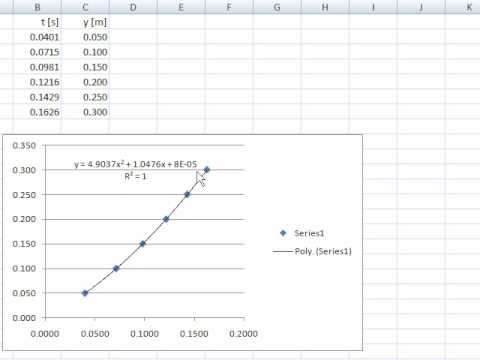
This should also include a column for the manual entry of distance measurements taken from the ruler. A series of results is accumulated in a table.
#DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB SOFTWARE#
Adding two small blobs of Blutack, at the lower corners, will improve the stability of the card as it falls.Ĭonfigure the data-logging software to measure the transit time and calculate the velocity as the card passes through the light gate. Measurements of the height fallen by the card should be made to this line rather than the lower or upper edge of the card. Draw a pencil line across the width of the card at exactly half its length. Clamp a ruler so that the vertical distance may be measured from above the level of the light gate.Ĭut black card to the precise length of 10.0 cm. Read our standard health & safety guidanceĬlamp the light gate about 20 cm above the bench. The emphasis of this datalogging experiment is on investigating the relationship between the velocity of the card and the distance it has fallen from rest. Thus you get the value of g in your lab setup.The acceleration of an object allowed to fall under the force of gravity is found by dropping a card vertically through a light gate. Then take an average value of the four g values found. So in this case for four data sets, you will get 4 values of g. Substitute each set of period (T) and length (L) from the test data table into the equation, and calculate g.
#DETERMINING THE ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB HOW TO#
Now for each of the 4 records, we have to calculate the value of g (acceleration due to gravity) Now see, how to calculate and what formula to use.

Table 1: Recording the following data for 4 sets of string length (1) Time for 10 oscillations & (2) Period (T) Calculating g (acceleration due to gravity) Record the data in the table below following the instructions in the section above.
Use a stopwatch to record the time for 10 complete oscillations. Move the mass so that the string makes an angle of about 5° with the vertical.Measure the effective length of the pendulum from the top of the string to the center of the mass bob.Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram:.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
